Mat2Str: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Business Rules!]] [[4.20]] introduces the '''Mat2Str''' [[internal function]] which converts an [[arrays|array]] to a [[string]] | [[Business Rules!]] [[4.20]] introduces the '''Mat2Str''' [[internal function]] which converts an [[arrays|array]] to a [[string]] | ||
mat2str(MAT <Array Name>, <String Variable> [, [MAT] <Delimiter$>] [, "<Quote-Type>] [:] [<trim>]") | |||
[[image:Mat2Str.png|800px]] | |||
===Parameters=== | |||
"MAT Array Name" is the source array, from which you are building a string. | |||
"String Variable" is the destination string that the function is creating. | |||
"MAT Delimiter$" is a character that will be put after every entry from the array including the last entry. The delimiter can be "" which would simply concatenate the array. It is optional. As of 4.3 it can be an array. | |||
"Quote Type" is optional, can be "Q", "QUOTES" , ' or " and is used to add quote processing to the string. This means that either a single or double quote will be placed around each of the source array's elements while creating the string. It's case insensitive. | |||
If Q or QUOTES is specified then BR determines which quote type to apply like this: If the first element is contained in quotes, the quotes are stripped and any two consecutive quotes of the same kind become singles. Next the element is scanned left to right for either type of quote character (single or double). If a quote character is encountered the element is enclosed in the alternate quote type and embedded occurrences of that quote type are doubled. If no quote character is encountered then double quotes are applied. | |||
"Trim" can be :LTRM , :TRIM or :RTRM and signifies the trim pre-processing of array elements. The colon is only used if preceded by a quote type. | |||
====Quote Processing Examples==== | |||
Quote Type is Q or QUOTES | |||
{|border="2" style="border-collapse:collapse;" | |||
|-style="background:#a5c7ff;" | |||
!Array Element | |||
!Part in the String | |||
!Explanation | |||
|- | |||
|abcdef | |||
|"abcdef" | |||
|Normal processing of double quotes | |||
|- | |||
|abc'def | |||
|"abc'def" | |||
|A single quote embedded in an array element remains embedded in the string | |||
|- | |||
|abc"def | |||
|'abc"def' | |||
|A double quote embedded in an array element remains embedded in the string | |||
|- | |||
|abc""def | |||
|'abc""def' | |||
|Embedded quotes are left intact when quotes are not active | |||
|- | |||
|'abcdef | |||
|"'abcdef" | |||
|One single quote will be included in the string's double quotes. | |||
|} | |||
Quote Type is ' (quote type single) | |||
When quote type is double, it mirrors quote type single. | |||
{|border="2" style="border-collapse:collapse;" | |||
|-style="background:#a5c7ff;" | |||
!Array Element | |||
!Part of the String | |||
!Explanation | |||
|- | |||
|abcdef | |||
|'abcdef' | |||
|Normal processing of double quotes | |||
|- | |||
|'abcdef | |||
|<nowiki>'''abcdef'</nowiki> | |||
|A leading single quote is duplicated when embedded in single quotes | |||
|- | |||
|"abcdef | |||
|'"abcdef' | |||
|Leading double quote is included within the single quotes, like any other character | |||
|} | |||
MAT2STR and [[STR2MAT]] trim outside of quotes but not inside of quotes. | |||
MAT2STR always adds quotes when quotes are present in the data. | |||
===Defaults=== | |||
1. The '''default Delimiter$''' is [[CR]] on Linux or [[CRLF]] on Windows. | |||
===Other=== | |||
1. Mat2Str performs the opposite action of [[Str2Mat]]. | |||
2. Remember to [[dim]]ension your resulting string. | |||
3. When using MAT2STR on a 2 dimensional array, the first delimiter is used for individual elements and the second delimiter at the end of each row. This principle also applies to arrays containing three to seven dimensions. For example, given the following two dimensional array zzz$ containing the values: | |||
1 2 | 1 2 | ||
3 4 | 3 4 | ||
The following statements- | The following statements- | ||
00010 Sep$(1)="," | |||
00020 Sep$(2)=hex$("0D0A") ! CRLF | |||
00030 MAT2STR( MAT zzz$, str$, MAT Sep$ ) | |||
00040 PRINT str$ | |||
Will produce- | Will produce- | ||
1,2 | 1,2 | ||
3,4 | 3,4 | ||
===Examples=== | |||
In the following code, we are making an array into a string separated by commas for printing. | |||
! make the codes into one string for printing | |||
let mat2str(Mat code$, MainString$, ",", "Q:trim") | |||
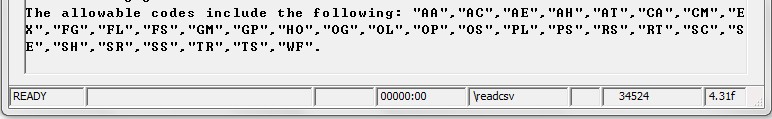
print "The allowable codes include the following: "&mainstring$&"." | |||
The output is as follows: | |||
[[file:readcsv.jpg]] | |||
Without the "Q:trim", it would appear like this: | |||
[[file:readcsv2.jpg]] | |||
Example 2: | |||
00010 dim resulting_String$*100, array$(3) | |||
00020 let array$(1)="first" | |||
00030 let array$(2)="second" | |||
00040 let array$(3)="third" | |||
00050 mat2str(mat array$,resulting_String$,"//") | |||
00060 print resulting_String$ | |||
Output: | |||
first//second//third | |||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
[[Category:Internal Functions]] | [[Category:Internal Functions]] | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:03, 28 August 2019
Business Rules! 4.20 introduces the Mat2Str internal function which converts an array to a string
mat2str(MAT <Array Name>, <String Variable> [, [MAT] <Delimiter$>] [, "<Quote-Type>] [:] [<trim>]")
Parameters
"MAT Array Name" is the source array, from which you are building a string.
"String Variable" is the destination string that the function is creating.
"MAT Delimiter$" is a character that will be put after every entry from the array including the last entry. The delimiter can be "" which would simply concatenate the array. It is optional. As of 4.3 it can be an array.
"Quote Type" is optional, can be "Q", "QUOTES" , ' or " and is used to add quote processing to the string. This means that either a single or double quote will be placed around each of the source array's elements while creating the string. It's case insensitive.
If Q or QUOTES is specified then BR determines which quote type to apply like this: If the first element is contained in quotes, the quotes are stripped and any two consecutive quotes of the same kind become singles. Next the element is scanned left to right for either type of quote character (single or double). If a quote character is encountered the element is enclosed in the alternate quote type and embedded occurrences of that quote type are doubled. If no quote character is encountered then double quotes are applied.
"Trim" can be :LTRM , :TRIM or :RTRM and signifies the trim pre-processing of array elements. The colon is only used if preceded by a quote type.
Quote Processing Examples
Quote Type is Q or QUOTES
| Array Element | Part in the String | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| abcdef | "abcdef" | Normal processing of double quotes |
| abc'def | "abc'def" | A single quote embedded in an array element remains embedded in the string |
| abc"def | 'abc"def' | A double quote embedded in an array element remains embedded in the string |
| abc""def | 'abc""def' | Embedded quotes are left intact when quotes are not active |
| 'abcdef | "'abcdef" | One single quote will be included in the string's double quotes. |
Quote Type is ' (quote type single) When quote type is double, it mirrors quote type single.
| Array Element | Part of the String | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| abcdef | 'abcdef' | Normal processing of double quotes |
| 'abcdef | '''abcdef' | A leading single quote is duplicated when embedded in single quotes |
| "abcdef | '"abcdef' | Leading double quote is included within the single quotes, like any other character |
MAT2STR and STR2MAT trim outside of quotes but not inside of quotes.
MAT2STR always adds quotes when quotes are present in the data.
Defaults
1. The default Delimiter$ is CR on Linux or CRLF on Windows.
Other
1. Mat2Str performs the opposite action of Str2Mat.
2. Remember to dimension your resulting string.
3. When using MAT2STR on a 2 dimensional array, the first delimiter is used for individual elements and the second delimiter at the end of each row. This principle also applies to arrays containing three to seven dimensions. For example, given the following two dimensional array zzz$ containing the values:
1 2 3 4
The following statements-
00010 Sep$(1)=","
00020 Sep$(2)=hex$("0D0A") ! CRLF
00030 MAT2STR( MAT zzz$, str$, MAT Sep$ )
00040 PRINT str$
Will produce-
1,2 3,4
Examples
In the following code, we are making an array into a string separated by commas for printing.
! make the codes into one string for printing let mat2str(Mat code$, MainString$, ",", "Q:trim") print "The allowable codes include the following: "&mainstring$&"."
Without the "Q:trim", it would appear like this:
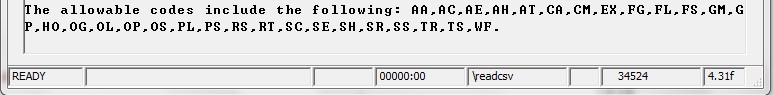
Example 2:
00010 dim resulting_String$*100, array$(3) 00020 let array$(1)="first" 00030 let array$(2)="second" 00040 let array$(3)="third" 00050 mat2str(mat array$,resulting_String$,"//") 00060 print resulting_String$
Output:
first//second//third