EOL: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
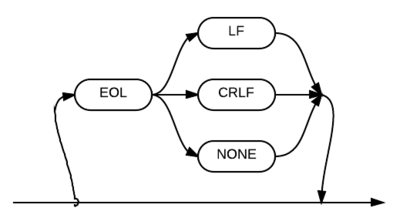
The "EOL=spec" parameter indicates the end-of-line separator for the data file being opened. The EOL keyword and equal (=) symbol are required. The "spec" keyword must be replaced with one of three options: LF (line feed), CRLF (carriage return, line feed and Ctrl-Z for end of file marker), or NONE. If either CRLF or LF is specified, then both are accepted as valid record delimiters for input; they are removed from incoming data. The syntax for this parameter can be inserted into any diagram that calls for the EOL=spec parameter. | The "EOL=spec" parameter indicates the end-of-line separator for the data file being opened. The EOL keyword and equal (=) symbol are required. The "spec" keyword must be replaced with one of three options: LF (line feed), CRLF (carriage return, line feed and Ctrl-Z for end of file marker), or NONE. If either CRLF or LF is specified, then both are accepted as valid record delimiters for input; they are removed from incoming data. The syntax for this parameter can be inserted into any diagram that calls for the EOL=spec parameter. | ||
EOL={LF|CRLF|NONE} | |||
[[Image:Eol.png|400px]]<br> | [[Image:Eol.png|400px]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 15:20, 7 May 2014
The "EOL=spec" parameter indicates the end-of-line separator for the data file being opened. The EOL keyword and equal (=) symbol are required. The "spec" keyword must be replaced with one of three options: LF (line feed), CRLF (carriage return, line feed and Ctrl-Z for end of file marker), or NONE. If either CRLF or LF is specified, then both are accepted as valid record delimiters for input; they are removed from incoming data. The syntax for this parameter can be inserted into any diagram that calls for the EOL=spec parameter.
EOL={LF|CRLF|NONE}
Defaults
- EOL=CRLF for DOS systems;
- EOL=LF for Unix / Linux systems.
Used in:
- Open statements