Type
The Type (TY) command sends the contents of a specified file to the screen, a printer, or another file.
Comments and Examples
Text files appear in a legible format when displayed with the Type command. The presence of non-alphabetic or non-numeric characters in other files, such as object program files, may make these files illegible.
however wildcard characters are not allowed in the file name that specifies the TYPE command.
The following example displays, one screen at a time, the contents of the file SAMPLE.ONE:
TYPE B:SAMPLE.ONE -P
The next command sends the same contents to a printer:
TYPE B:SAMPLE.ONE PRINT
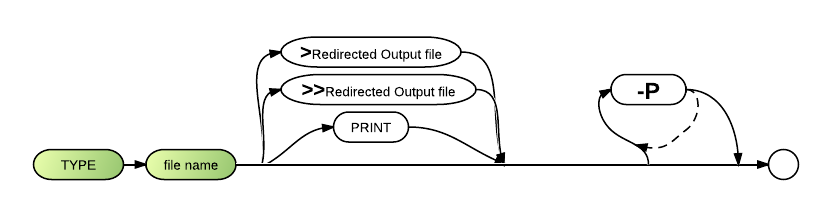
Syntax
TYPE <file name> [{[>[>]<output file>|PRINT}][-P]
Defaults
- Display the information on the screen.
- Scroll entire contents of file without pausing.
Parameters
The TYPE command requires the file name parameter, which specifies which file the system should display on the screen or send to a printer or file.
The optional >redirected output file parameter indicates the file or device to which the contents of the specified file should be sent. One redirection arrow causes the information to be written over any data that previously existed in the file. Two redirection arrows >> causes the information to be appended to the end of the file.
PRINT, which operates the same as >PRN:, sends the contents of the specified file to a printer rather than to the screen.
Note that TYPE PRINT does not utilize printer substitutions, but Ctrl-P does.
The -P option causes scrolling to pause after the typed contents of the file fills one screen.
Comments
- TYPE now works on locked files.
- TYPE PRINT no longer inserts carriage returns in long print lines, unless they are going to the screen. This was fixed earlier for files. Now it is fixed for typing to printers as well.
Note that TYPE skips the header portion of Internal files)