Input Fields: Difference between revisions
(→Syntax) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
===Parameters=== | ===Parameters=== | ||
See | See [[Screen I/O]] for complete descriptions of the parameters for INPUT FIELDS. | ||
{{Input Fields Parameters}} | {{Input Fields Parameters}} | ||
Revision as of 20:40, 22 January 2013
The Input Fields (IN F) statement uses the capabilities of full screen processing to set up fields for input and to accept input from anywhere on the screen. The input fields may utilize a wide variety of display and control attributes. In addition, the Input Fields statement uses the capabilities of field help windows to set up help messages for any or all of the fields it defines.
See also: Screen Attribute
Comments and Examples
Input Fields accepts data from anywhere on the screen except the status line. One field or several fields may be entered with the INPUT FIELDS statement.
PRINT FIELDS, INPUT FIELDS, RINPUT FIELDS, INPUT SELECT and RINPUT SELECT all utilize full screen processing and field help windows. See the Screen I/O for examples common to all of these statements.
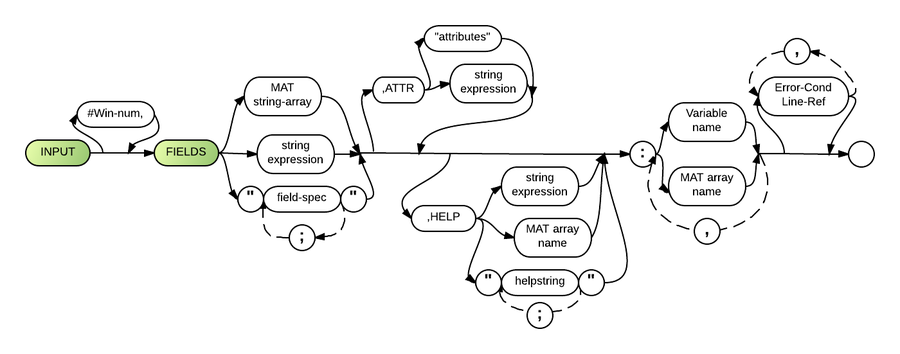
Syntax
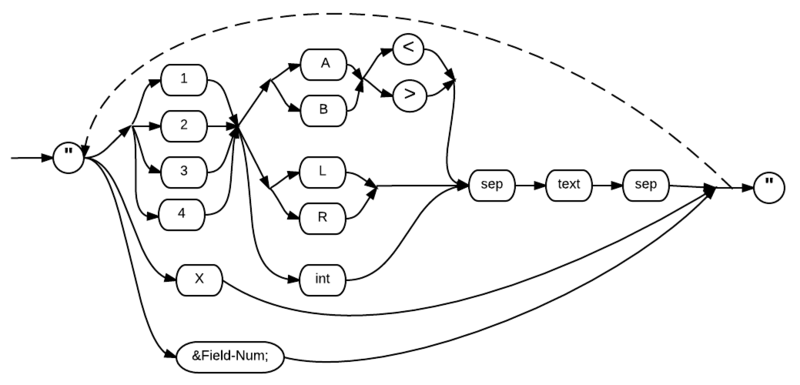
Note that in the "field-spec" and "helpstring" parts, multiple values are separated by semi-colons and are placed within the quotation marks together (i.e. "item;item;item"). In the MAT array-name part, multiple values are separated by commas and there are no quotation marks.
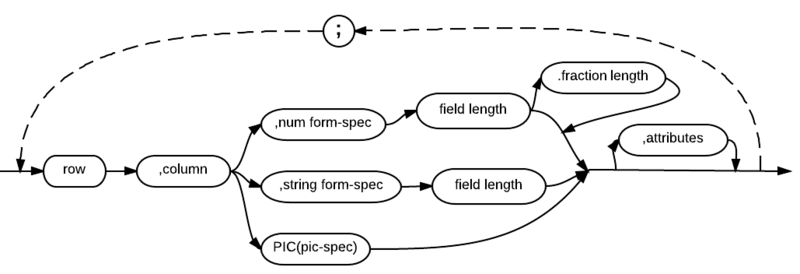
Supplemental Syntax ("field-spec" parameter)
Supplemental Syntax ("helpstring" parameter)
Defaults
- 1.) Display to and input from the screen.
- 2.) Do not alter attribute when field is current.
- 3.) Do not display field help text.
- 4.) Interrupt the program if an error occurs and "ON error" is not active.
- 5.) Fraction length = 0.
- 6.) Maximum DIM length.
- 7.) Use current attributes.
- 8.) Center window above field.
- 9.) R if possible; attempt B, L, then A if necessary.
Parameters
See Screen I/O for complete descriptions of the parameters for INPUT FIELDS.
The "field-spec" supplemental syntax may be inserted where the "field- spec" parameter appears in the main diagram for full screen processing statements. If the "string-expr" or "MAT string-array" parameters are used to specify the field definition, each must include the same elements that are identified in the "field-spec" parameter.
The "row" parameter is a required integer value that indicates the row number on the screen or in the window where the data is to be entered.
The "column" parameter is a required integer value that indicates the starting column number on the screen where data is to be entered.
The next set of parameters specifies the format type of the data to be entered. There are three possible routes. In the top route, "num form-spec" represents a numeric format specification. G, GL, GU, GZ, L, N, and NZ are all valid in this position; the specification must be followed by a space. The "field-length" parameter, which is an integer value that identifies the length (including decimal point and decimal positions) of the field comes next. If the field contains decimal positions, "fraction" should identify how many there are; this parameter must be separated from the field length by a period (no spaces).
In the middle route, "string form-spec" represents a string format specification. C, CC, CR, CL, CU, G, GL, GU, GZ, V, VL and VU are all valid in this position. If "field length" is used, it must be separated from the format spec by a space.
In the bottom route, the "PIC" or "FMT" specification allows you to specify a picture of the field to be input. See File I/O for a list of the characters that may be used in the "(pic-spec)" portion of this parameter.
See Format Specifications for additional information about all the format specifications listed in this section.
The "attributes" parameter represents an insertable syntax that identifies the monochrome, color and control attributes that are to be used for the field. See Attribute (Screen) for details.
Additionally, fonts can be controlled at the field level by assigning them to attribute substitution letters as in:
CONFIG ATTRIBUTE [J],font=ariel,slant,max
This specifies ariel italics maximum size.
Technical Considerations
- 1.) Relevant error conditions are: CONV, ERROR, EXIT, HELP, IOERR, and SOFLOW.
- 2.) When OPTION INVP is in effect, normal input of commas and periods is interchanged in PIC, N, NZ, L, G and GZ format specifications to support European- style numbers.
- 3.) For specific information about inputting or outputting multiple fields in a single statement, see the Screen I/O chapter.
- 4.) See the Chapter 19 - Functions chapter for information about CNT, which applies to errors in field definition arrays used in full screen processing. CNT returns the number of the last successfully processed variable or the last successfully compiled element of the array.
- 5.) See CURFLD, which returns the relative number of the field containing the cursor from the last INPUT FIELDS statement.
- 6.) When PIC is used with INPUT FIELDS for numeric input and all digit specifiers are "#", the cursor will automatically skip over non-numeric characters which are displayed in the field. In the following example, line 20 creates an output field of eight positions, but the operator will only be able to key in the six numeric positions:
- | 00020 INPUT FIELDS "5,10,PIC(##/##/##),r": D
- 7.) Uppercase or lowercase conversion upon input is available when the C, V or G format specifications are followed by either a U (convert to uppercase) or an L (convert to lowercase). See the CL, CU, GL, GU, VL and VU format specifications in the File I/O chapter for more information.
- 8.) When RETRY is executed after an error has occurred in an INPUT FIELDS statement, the cursor is automatically positioned at the start of the field which caused the error.
- 9.) Keyboard buffering operates identically for INPUT FIELDS as it does for INPUT. Buffering may be turned on or off with the BRConfig.sys file TYPEAHEAD specification.
- 10) Using an alpha character for field length in INPUT FIELDS or PRINT FIELDS will now produce an error. Previously the characters as well as the attributes following it were being ignored. (This may affect your programs). Extraneous characters in attribute specifications will still be ignored.
- 11.) The FMT specification is now supported for validating and formatting of entered data. See "FMT" Spec in the Format Specification section for complete information.
- 12.) A special hot-key value (trailing attribute spec in FIELDS operation) of 10000 denotes the Enter key, and generates a zero fkey value.
- 13.) Hot field fkey values may now be in the ranges
- 1-128 (Note - 90-99 may be assigned special functions in BR.)
- 1000-9999
- 14.)Use INPUT FIELDS ... NOWAIT to raise a TAB.
- 15.) The ATTR parameter in FIELDS and SELECT statements now accepts MAT variables. This feature allows for a different "current" attribute for each input field. Thus if using INPUT SELECT to select many items from a list, the non-current and current attributes may be different for both selected and un-selected items. NOTE the following sample syntax:
00100 INPUT FIELDS MAT F$, ATTR MAT FF$:MAT DATA$
MAT FF$ is compiled for attributes ONLY, and stops at the end of the array or the first error. If there are not enough attributes for each entry field, the first one will be used. For an example of this feature in action, enter and execute the following sample program:
00100 ! matattr ! example of ATTR MAT attrs specification 00110 PRINT NEWPAGE 00120 PRINT FIELDS "1,2,c 30,/RGBH:R": "[F6]-End selections" 00130 DIM ATTRS$(15),SPEC$(15),DATA$(15)*8 00140 FOR I=1 TO UDIM(ATTRS$) ! set up mats 00150 LET ATTRS$(I)="U/RGB:R" 00160 LET SPEC$(I)=STR$(I+3)&",10,c 8,N/RGB" 00170 READ DATA$(I) : LET SEL$=SEL$&" " 00180 NEXT I 00190 DATA One,Two,Three,Four,Five,Six,Seven,Eight,Nine,Ten,Eleven,Twelve,Thirteen,Fourteen,Fifteen 00200 RINPUT SELECT MAT SPEC$,ATTR MAT ATTRS$: MAT DATA$ 00210 IF CMDKEY>0 THEN GOTO 250 00220 LET ATTRS$(CURFLD)="HU/RGBH:R" : LET CURFLD(CURFLD) : LET SPEC$(CURFLD)=SREP$(SPEC$(CURFLD),",N/RGB",",UHR/HRGB") !:! change attributes of selections 00230 LET SEL$(CURFLD:CURFLD)="x" ! could reverse logic of prev. line to unselect 00240 GOTO 200 00250 ! 00260 FOR I=1 TO LEN(SEL$) 00270 IF SEL$(I:I)<>" " THEN PRINT DATA$(I);" "; 00280 NEXT I
Window On A Field
The ability to enter and process more text than a window field can display at one time is included. This is a very powerful feature that lays the groundwork for support of proportional fonts. You will, for example, be able to enter and maintain fifty characters of data in a ten character window field on any platform.
The syntax for enabling this capability is:
INPUT FIELDS "xx,yy,8/C 12,UH": name$
Which enables up to 12 characters to be entered into an 8 character window field.
This syntax was changed in version 4.17. Formerly window on a field syntax was "xx,yy,C 8/12,UH":name$
Mat Grouping
MAT grouping is allowed in all full screen-processing statements. This feature allows you to indicate that input or output should alternate between all MAT variables which are specified within parentheses in the I/O list.
In the following code fragment, the A$ variable identifies the positions on the screen from which input values should be drawn. Business Rules will assign the first input value to the first element of B$. However, because the B$ and C matrices are specified within parentheses, it will then assign the second input value to the first element of C. The third value will go to B$, the fourth to C, and so on until both matrices are fully assigned. The last input value will go to X$.
00020 INPUT FIELDS A$: (MAT B$,MAT C),X$
Without MAT grouping, the above line must be coded as follows in order to achieve the same results (this example assumes that B$ and C have each been dimensioned for five elements):
00020 INPUT FIELDS A$: B$(1),C(1),B$(2),C(2),B$(3),C(3),B$(4),C(4),B$(5),C(5),X$
MAT grouping is a lot easier to code, it executes faster, and most important it handles much larger arrays than are possible without using MAT grouping, as the resulting compiled line takes up less space in memory. The number of matrices that can be grouped together is 62, which in practical terms are no limit. All matrices in a group must have the same number of elements per matrix, or an error 0106 will result. Only MAT variables may be used in such groupings.
Also see Error 0106 in ERROR CODES section of the manual for additional information.
Timeout (Wait) Processing
The WAIT= parameter and TIMEOUT error trap may now be used with INPUT/RINPUT statements to force releasing of records. This feature is useful for multi-user situations.
WAIT= specifies the number of seconds the system should wait for operator input before responding with a TIMEOUT error condition. Note that WAIT=0 instructs the system to wait for zero seconds, not to ignore the WAIT instruction. Also, -1 is a special WAIT value that instructs the system to wait forever, if necessary. Every time the operator presses any key, the clock is reset for WAIT seconds.
00100 INPUT WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100 00110 RINPUT WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100 00120 LINPUT WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100 00130 INPUT FIELDS "10,10,C 10",WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100 00140 INPUT #11,FIELDS "10,10,C 10",WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100 00150 RINPUT FIELDS "10,10,C 10",WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100 00160 INPUT SELECT "10,10,C 10",WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100 00170 RINPUT #11,SELECT "10,10,C 10",WAIT=10:X$ TIMEOUT 100
The TIMEOUT error condition traps time-out errors (error code 4145) and specifies the line number of an appropriate error- handling routine.
0100 RELEASE #ITEM: 00110 PRINT "OVER TIME LIMIT" 00120 PRINT "Your hold on inventory items has expired, re-enter order."
Before releasing the record, you may want to go to a routine that warns with a message and a few beeps that the hold on records is about to be released, then gives the operator an opportunity to continue data entry. See the KStat$ internal function for information on how to use the WAIT parameter with that function.
Feature Deletion
Formerly the FIELDS trailing attribute supported specification of an X'xx' scancode. This caused considerable confusion because the value produced was translated to its functional equivalent for fkey purposes (e.g. X'02' became fkey 90 - pgup).
This hex scancode capability has been removed as of this release.
It is necessary to specify only numeric values for trailing attribute hot key values. These values correspond to FKEY results that are produced by clicking on the hot field.
NxtRow, Next and NxtCol
The NxtRow, Next, and NxtCol internal functions we're introduced in BR! 4.20.
The keyword Next can be used in the same manner as CUR in that the next cursor position within a 2D control can be identified.
00100 INPUT FIELDS "row,col,GRID 10/60, SUB, NEXT, NOWAIT": next_pos
The NxtRow is a internal function that identifies the character position or cell row associated with the next cursor position (e.g. where the mouse was last clicked). If the next cursor position is in a 2D control, then NxtRow specifies the row of the cell within the 2D control. If not it specifies the first character position of the next control to receive focus.
NxtCol specifies the column of the respective position.
With respect to these functions, the next cursor position can be the result of keyboard or mouse activity. If the next position results from keyboard activity then NxtRow has the same value as CurRow when Enter is pressed or control was returned in response to a leading attribute such as X (return control upon exit). When the mouse is used to return control to a program, the next cursor position is the pointer location that is double clicked or hot location that is single clicked.
One key concept here is that just as one must keep track of what type of control was last accessed, by means other than CurRow and CurCol, similarly **one must determine the type of control to be next accessed by means other than NxtRow and NxtCol**. This can be done with the system function NxtFld plus hotkey event (fkey) numbers.